Used with high contrast subjects, High Dynamic Range (HDR) preserves details in highlights and shadows by combining two shots taken at different exposures. Use with high-contrast scenes and other subjects to preserve a wide range of details, from highlights to shadows.

|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
[] |
|
|
[] |
Choose the difference in exposure between the two shots. The higher the value, the greater the dynamic range. If [] is selected, the camera will automatically adjust the exposure differential to suit the scene. |
|
[] |
Choose how much the boundaries between the two images are smoothed. |
|
[] |
Choose [] to save each of the individual shots used to create the HDR image; the shots are saved in NEF (RAW) format. |
Taking HDR Photographs
We recommend that you use the matrix metering option when shooting with HDR.
-
Highlight [] in the photo shooting menu and press 2.
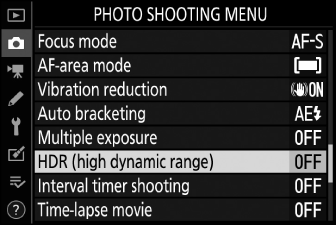
-
Select an [].

-
Highlight [] and press 2.
-
Highlight one of the following options using 1 or 3 and press J.
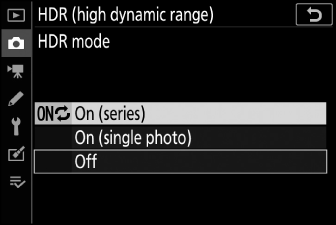
Option
Description
0
[]
Take a series of HDR photographs. HDR shooting will continue until you select [] for [].
[]
Normal shooting will resume after you have taken a single HDR photograph.
[]
Proceed without taking additional HDR photographs.
-
If [] or [] is selected, an icon will appear in the display.
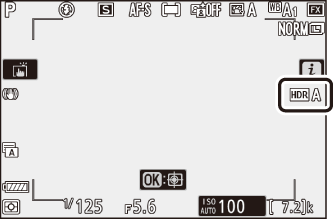
-
-
Choose a value for [].

-
Highlight [] and press 2.
-
Highlight an option using 1 or 3 and press J.

-
Choose higher values for high-contrast subjects.
-
Note, however, that choosing a higher value than required may not produce the desired results. Match your choice to the level of contrast in the scene.
-
If [] is selected, the camera will automatically adjust the exposure differential to suit the scene.
-
-
Adjust [].

-
Highlight [] and press 2.
-
Highlight an option using 1 or 3 and press J; the selected option represents the amount the boundaries between the two images are smoothed.

-
Higher values produce a smoother composite image.
-
-
Choose a setting for [].

-
Highlight [] and press 2.
-
Highlight an option using 1 or 3 and press J.
-
Choose [] to save each of the individual shots used to create the HDR image; the shots are saved in NEF (RAW) format.
-
-
Frame the photograph, focus, and shoot.
-
The camera takes two exposures when the shutter-release button is pressed all the way down.
-
If [] is selected for [], you can continue to take HDR photographs until [] is selected.
-
If [] is selected, HDR will turn off automatically after a single shot.
-
HDR photographs are recorded in JPEG format regardless of the option selected for image quality.
-
-
The edges of the image will be cropped out.
-
The desired results may not be achieved if the camera or subject moves during shooting. Use of a tripod is recommended.
-
Depending on the scene, you may notice shadows around bright objects or halos around dark objects. This can be mitigated using [].
-
Uneven shading may be visible with some subjects.
-
With spot or center-weighted metering, an [] of [] is equivalent to [].
-
Optional flash units will not fire.
-
In continuous release modes, only one photograph will be taken each time the shutter-release button is pressed all the way down.
-
Shutter speeds of “Bulb” and “Time” are not available.
HDR cannot be combined with some camera features, including:
-
modes other than P, S, A, and M,
-
flicker reduction,
-
bracketing,
-
multiple exposures,
-
interval-timer photography,
-
time-lapse movie recording, and
-
focus shift
